How I AI: Cognition Labs CEO Scott Wu & Devin AI, the junior engineer that never sleeps
Learn three game-changing AI workflows from Scott Wu, CEO of Cognition Labs, showing how to leverage Devin AI for faster, more efficient software development, from handling routine tasks to managing complex projects.
Claire Vo
In this episode, I got a live demo from Scott Wu, the CEO and founder of Cognition Labs. They’re the team behind Devin, an AI agent that acts like a junior engineer on your team. Scott shared some practical, real-world workflows that are changing how his team builds software. He and his team use AI, and Devin specifically, to make their engineering process more efficient. The goal isn't to replace human engineers, but to free them up to focus on the truly complex challenges while Devin handles more routine tasks. If you're looking to get more out of your software development process, this episode (and this post) has some great ideas.
Scott is an expert at building AI tools that solve actual problems for engineers. You can hear his passion when he talks about Devin—not just as a piece of software, but as a collaborative team member that works asynchronously alongside human engineers. We’ll walk through three key workflows Scott showed me, which demonstrate how Devin fits into different stages of the development lifecycle. The common thread is that Devin acts as a highly efficient, always-on junior engineer, capable of tackling everything from small frontend fixes to more involved integrations.
Workflow 1: Integrating a New Server using Devin and DeepWiki
This first workflow tackles a common engineering problem: integrating a new server into an existing codebase. It’s a great example of how Devin can handle a well-defined task, freeing up senior engineers for more strategic work. What makes this so effective is the combination of smart research (using DeepWiki) and a well-written prompt to guide Devin's actions.
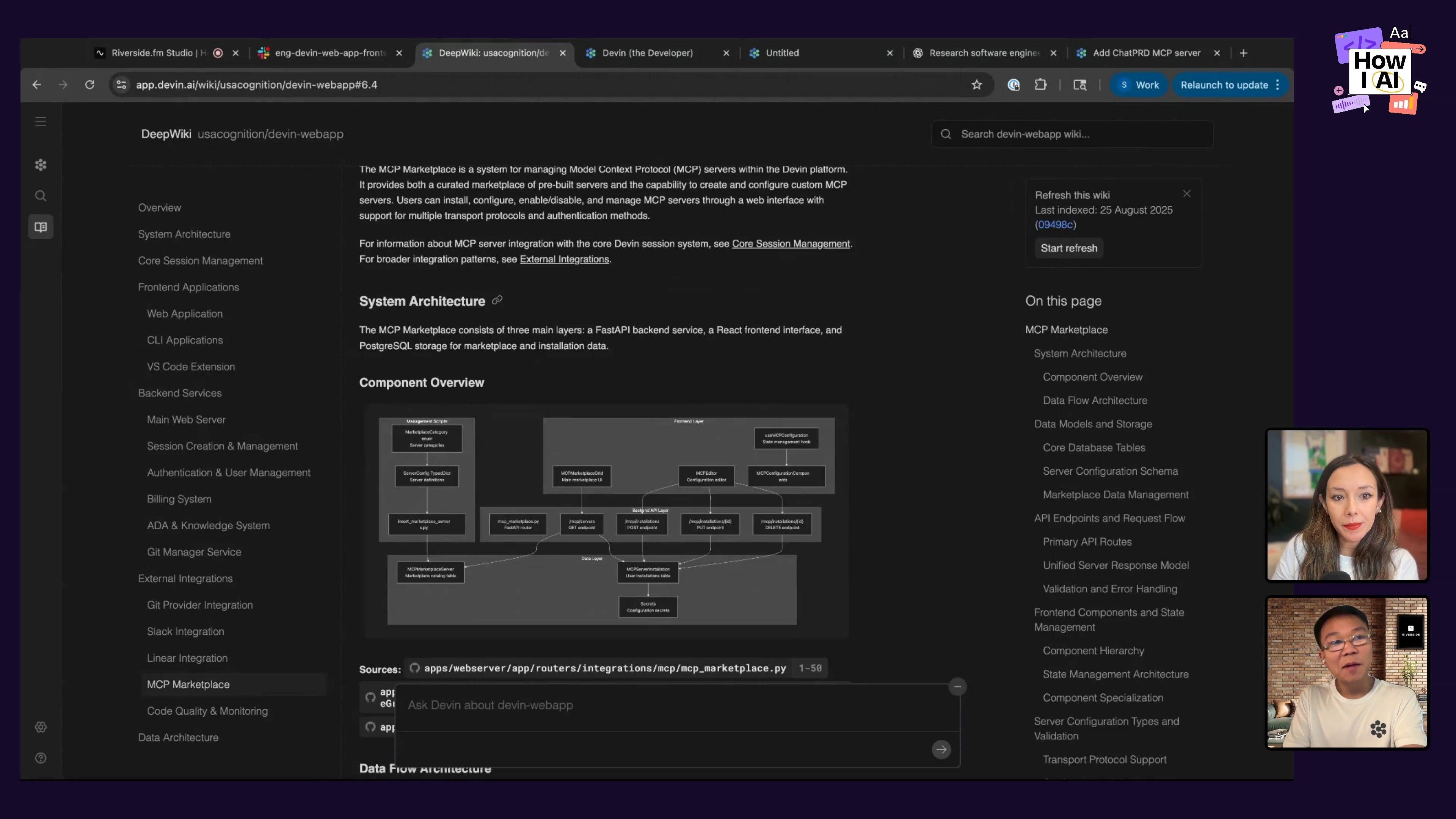
Step 1: Understanding the Codebase with DeepWiki
Scott started by using DeepWiki, an AI-powered tool that generates documentation, to get a handle on the relevant section of his codebase. This tool automatically creates natural language explanations and code snippets, which is much faster than trying to understand a complex system by manually reading the code.
Step 2: Crafting the Devin Prompt
Instead of giving Devin a simple, vague instruction, Scott used what he learned from DeepWiki to create a prompt with a lot of context. This part is really important; a good prompt helps Devin understand the task completely and produce the right result. Here’s the prompt he used:
Please go research the chat PRD-MCP server and add that to the list here. Follow the pattern of existing servers like Atlassian and HubSpot. Here's the exact type it structure that would be used here. Here are the functions that you should be looking at. And here's what you should check to make sure that it works.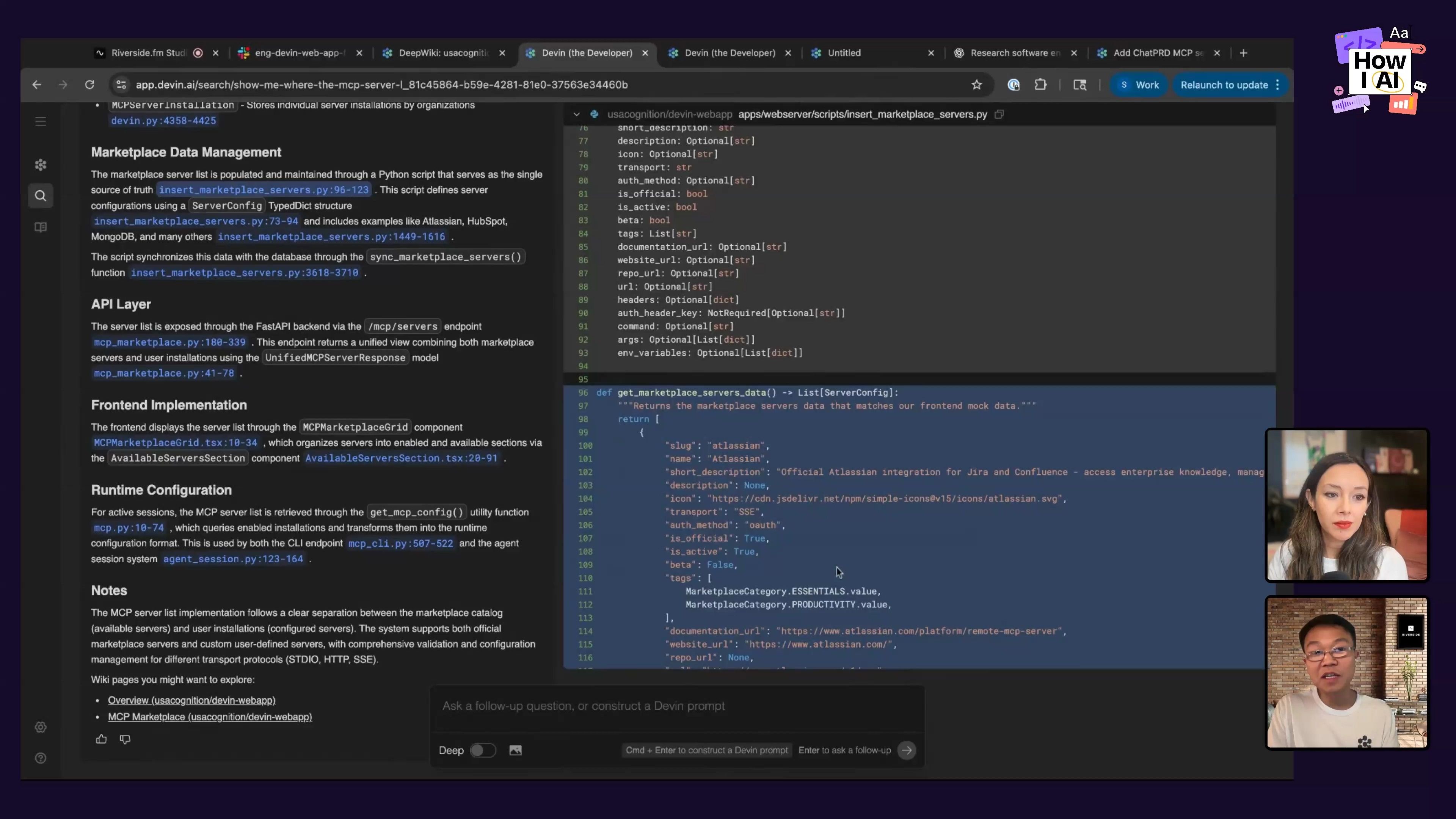
Step 3: Asynchronous Execution and Pull Request Generation
After he kicked off the Devin session, the work continued in the background. Devin does the research, writes the code, tests it, and even opens a pull request (PR) on GitHub. This lets Scott move on to other things, like attending meetings or working on another project, while Devin handles the integration.
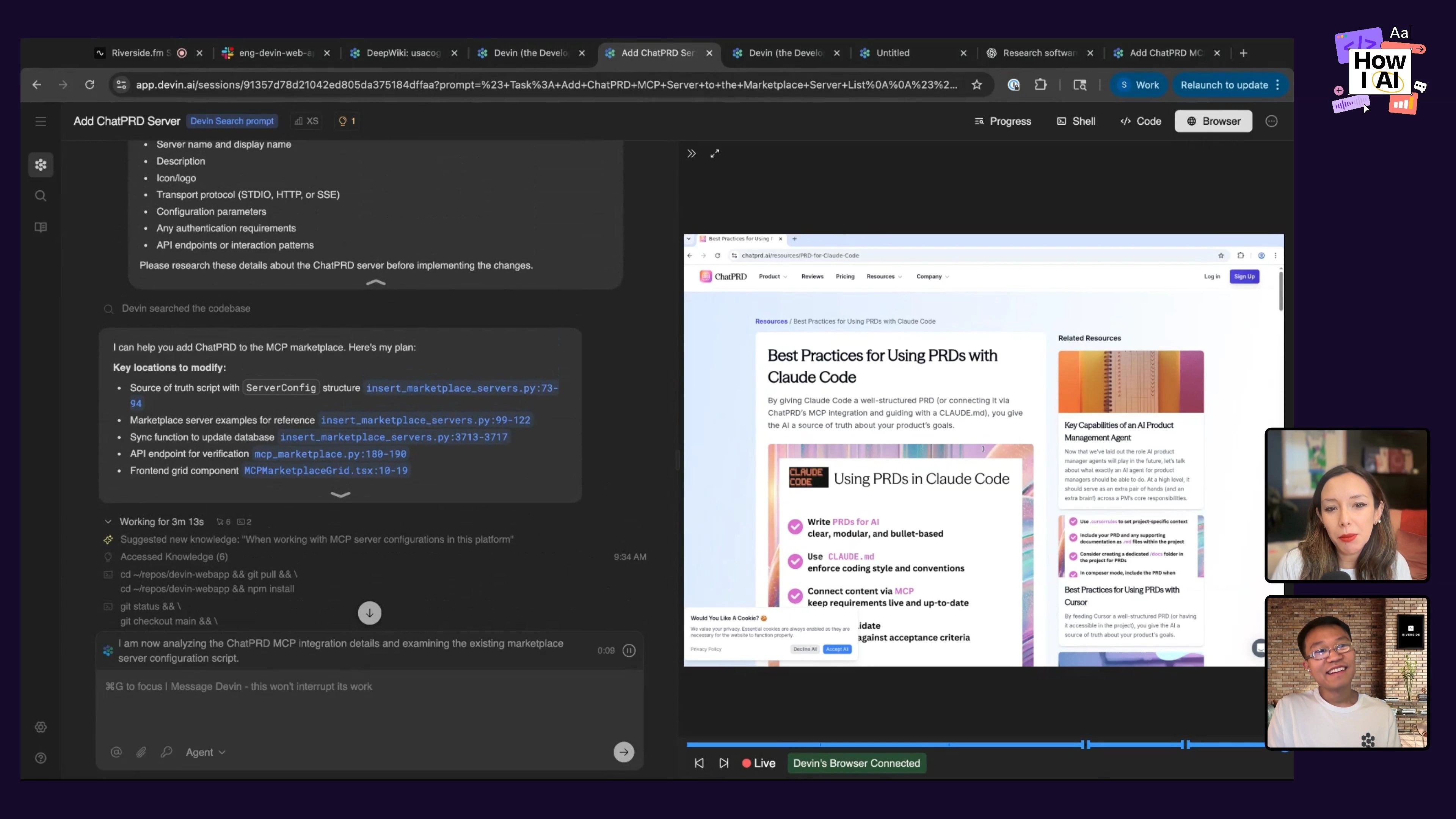
Step 4: Review and Merge
Once the PR is ready, Scott can review the changes Devin made and give feedback if needed. It’s a collaborative process that maintains quality control while being incredibly efficient.
Workflow 2: Handling Frontend Fixes with Devin
This next workflow is all about using Devin for quick frontend fixes and adjustments. It’s a great way to use Devin as an always-available resource for polishing a product's user interface. The speed is pretty amazing, allowing for really fast iteration and improvements.
Step 1: Identifying the Task
This workflow starts by identifying a specific frontend issue, like adjusting a button's size, spacing, or style. Sometimes this involves using a screenshot to clearly show the desired changes.
Step 2: Devin's Role
Devin gets the task of making the frontend adjustments. It finds the relevant code, implements the changes, and often provides before-and-after screenshots to make the review process quick and easy. This cuts down on the back-and-forth between engineers, saving a lot of time.
Step 3: Review and Feedback
Scott (or another team member) then looks over the changes Devin proposed and offers feedback if necessary. Because the process is so fast, the team can make rapid improvements to the user experience.
Workflow 3: Establishing Devin as a First Line of Defense for Incidents
This last workflow shows how Devin can be used for incident response, which can seriously cut down on response times and improve overall system reliability. It's a proactive way to use AI to keep issues from getting worse.
Step 1: Integrating Devin into the Alert System
Devin is hooked into the team's alert system, like PagerDuty. When a crash or another incident happens, Devin is automatically alerted and starts investigating.
Step 2: Devin's Incident Report
Devin analyzes logs, traces the error, and puts together an initial incident report that is immediately sent to the human engineers. This report often pinpoints the likely cause of the issue, helping the team triage the problem right away.
Step 3: Collaborative Investigation and Resolution
Human engineers can then take Devin's report, use the information to investigate further, and work together to fix the problem. Devin provides a huge head start, making the entire resolution process much faster and more efficient.
Conclusion
Scott's workflows really highlight how AI can be a genuine partner in software development. Devin is more than just a tool; it's a collaborative team member that can handle tasks, speed up development, and let human engineers focus on higher-level, more creative problems. By combining AI agents like Devin with smart prompting and a collaborative mindset, Scott's team is showing what the future of building software can look like. I hope you'll try out some of these ideas and experiment with your own AI-powered workflows. The future of software engineering feels very collaborative, and AI is going to be a big part of it. Give these workflows a shot, and let me know how it goes!
Sponsor Thanks
This episode is sponsored by:
- Google Gemini: Google Gemini is a powerful new AI model that can help you with a wide range of tasks, from writing code to creating art.
- Vanta: Vanta automates compliance and simplifies security, so you can focus on building your product.
Episode Links
Try These Workflows
Step-by-step guides extracted from this episode.

How to Set Up Devin AI for Automated Incident Response and Triage
Integrate Devin AI with your alerting system like PagerDuty to act as a first responder for incidents. Devin automatically investigates issues, analyzes logs, and generates an initial report to accelerate triage and resolution by your engineering team.

How to Use Devin AI for Rapid Frontend UI Fixes and Iteration
Leverage Devin AI as an always-available resource to quickly handle frontend UI adjustments like button styling or spacing. Devin implements the changes and provides before-and-after visuals, drastically speeding up the review and iteration cycle.

How to Integrate a New Server into a Codebase with Devin AI and DeepWiki
Use Devin AI as a junior engineer to integrate a new server into an existing codebase. This workflow combines DeepWiki for codebase analysis and a detailed prompt to guide Devin, which then handles research, coding, and pull request generation asynchronously.


